38 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
The Parts Of An Animal Cell - Science Trends There are 13 main parts of an animal cell: cell membrane, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, centrioles, cytoskeleton, vacuoles, and vesicles. A cell is the smallest unit of life; cells tend to be 1 - 100 micrometers (μm) in diameter, and each cell, while ... Solved In eukaryotic cells, the processes of protein ... In eukaryotic cells, the processes of protein synthesis occur in different cellular locations. Drag the labels to the appropriate targets to identify where in the cell each process associated with protein synthesis takes place. Part B - Roles of RNA in protein synthesis in eukaryotes. RNA plays important roles in many cellular processes ...
10 Examples of Eukaryotic Cells with Pictures - Study Read Typical eukaryotic cell examples include. 1. Animal cells. All animal cells are eukaryotic in nature. There are billions of cells in animals, and all of them are eukaryotic. 2. Sperm cells. Sperm cells will tail to swim in the uterus. This is also an animal cell with haploid chromosomes.
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.
Interactive Eukaryotic Cell Model - CELLS alive Solve the Cell Model Jigsaws. Nucleus: The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. It is enclosed in a double membrane and communicates with the surrounding cytosol via numerous nuclear pores. Within each nucleus is nuclear chromatin that contains the organism's genome. The chromatin is efficiently packaged within the ... Cell Organelles - Types, Structure and their Functions The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle, which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cell's DNA. By structure, the nucleus is dark, round, surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic Cell Parts, Functions & Diagram Eukaryotic Cell Envelope & External Structures Cell Wall: The cells of plants, algae and fungi have thick, protective cell walls, which provide support, help maintain the shape of the cell, and prevent the cell from taking in too much fresh water and bursting.
Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell.. SOLVED:Label the lettered parts of this eukaryotic cell. Label the lettered parts of this eukaryotic cell. · A. Cell membrane. B. Nuclear membrane. C. Nucleolus D. Mitochondria E. Centriole F. Endoplasmic reticulum. G.5 answers · Top answer: on the right side here. I have listed some of the major structures of the Eukaryotic, so and ... Eukaryotic Cells - Visible Body Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally have a nucleus —an organelle surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope —where DNA is stored. There are a few exceptions to this generalization, such as human red blood cells, which don't have a nucleus when mature. Organelles of Eukaryotic Cells - Windows to the Universe The "brains" of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA. Mitochondria. Make energy out of food. Ribosomes. Make protein. Golgi Apparatus. Make, process and package proteins. Lysosome. Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down. Eukaryotic Cells - Definition, Parts, Examples, and Structure Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles. Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells.
Quia - Cell Parts and Functions The parts of a cell with a particular function: Prokaryotic: Cells with no true nucleus and no membrane bound organelles: Eukaryotic: Cells that contain a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles: Centrioles: Only in animal cells, aid in cell division: Ribosomes: Produce Proteins: Chloroplast: Found only in plants, site of photosynthesis ... 3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells ... Nucleus. Unlike prokaryotic cells, in which DNA is loosely contained in the nucleoid region, eukaryotic cells possess a nucleus, which is surrounded by a complex nuclear membrane that houses the DNA genome (Figure 3.59).By containing the cell's DNA, the nucleus ultimately controls all activities of the cell and also serves an essential role in reproduction and heredity. Label the cell structure. | Study.com Eukaryotic cells, including human cells, contain a nucleus (with the exception of red blood cells) and organelles. Organelles are membrane-enclosed structures ...1 answer · Top answer: A. Cytosol B. Plasma Membrane C. Mitochondrion D. Nucleus E. Chromatin F. Endoplasmic Reticulum G. Lysosome H. Free Ribosome I. Golgi... Eukaryotic Cells | Biology I - Lumen Learning The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (Figure 4) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, and vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly.
Important Parts of Eukaryotic Cells - dummies All eukaryotic cells have organelles, a nucleus, and many internal membranes. These components divide the eukaryotic cell into sections, with each specializing in different functions. Each function is vital to the cell's life. The plasma membrane is made of phospholipids and protein and serves as the selective boundary of the cell. 3.3 Eukaryotic Cells - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian ... The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. PDF Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells - Grosse Pointe Public Schools The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform all necessary functions of life. Certain functions are carried out within different structures of the cell. These structures are called organelles. Model 1 - How Is a Cell Like a Factory? Part of factory Cell organelle Function Control ... identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell ... Sep 10, 2020 — Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ identify and label each part of the eukaryotic cell.1 answer · 3 votes: heres your diagram with labeling
Eukaryotic Cell Labeling Diagram - Quizlet Eukaryotic Cell Labeling STUDY Learn Write Test PLAY Match + − Created by tasheia_floyd Terms in this set (20) Nuclear Envelope ... Nucleus ... Chromatin ... Nucleus ... Ribosomes ... Golgi Apparatus ... Lysosome ... Mitochondira ... Peroxisome ... Microvilli ... Microtubules ... Intermediate Filaments ... Microfilaments ... Cytoskeleton ...
Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells | Microbiology The cytoskeleton is a network of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules found throughout the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. In these fluorescently labeled animal cells, the microtubules are green, the actin microfilaments are red, the nucleus is blue, and keratin (a type of intermediate filament) is yellow.
Solved PART 1 1. Identify the major similarities and ... PART 1. 1. Identify the major similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 2. Where is the DNA housed in a prokaryotic cell? Where is it housed in a eukaryotic cell? 3. Identify three structures which provide support and protection in a eukaryotic cell. PART 2. 1. Label each of the arrows in the following slide image:
Label Eukaryotic Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Start studying Label Eukaryotic Cell. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell - Brainly.com answered Identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell Advertisement Answer 2 rawan12343 can you take a picture so I can help you identify it. Still stuck? Get 1-on-1 help from an expert tutor now. yes the nucleus would be your answer. Advertisement Answer 5.0 /5 5 jenniferlove131418 Answer: Label A nucleus Label B cytoplasm Label C
Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes - Kenhub The first is the cell nucleus, which houses DNA in the form of chromosomes. The second is the cytoplasm, a thick solution mainly comprised of water, salts, and proteins. The parts of a eukaryotic cell responsible for maintaining cell homeostasis, known as organelles, are located within the cytoplasm.
BYJU'S Online learning Programs For K3, K10, K12, NEET ... BYJU'S Online learning Programs For K3, K10, K12, NEET ...
The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf The division cycle of most eukaryotic cells is divided into four discrete phases: M, G1, S, and G2. M phase (mitosis) is usually followed by cytokinesis. S phase is the period during which DNA replication occurs. The cell grows (more...) The duration of these cell cycle phases varies considerably in different kinds of cells.
Eukaryotic Cells: Types and Structure (With Diagram) 1. Undifferentiated Cells: ADVERTISEMENTS: These unspecialized cells are capable of undergoing division and development. For example, Zygote, stem cells (in animals) and meristematic cells (in plants) 2. Differentiated cells (- Post-mitotic cells): These are specialized cells which perform a specific function and exhibit division of labour.




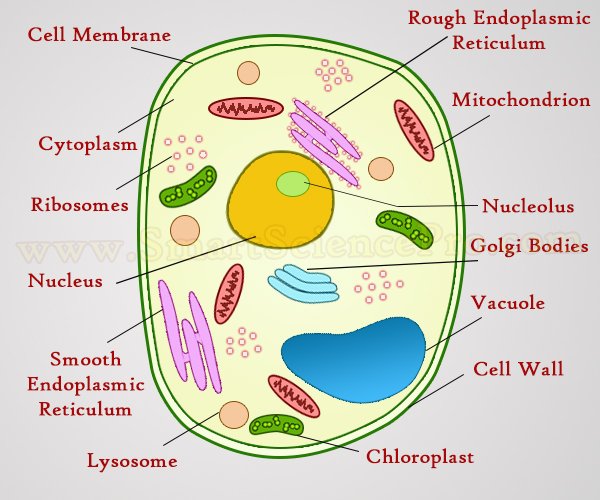


Post a Comment for "38 identify and label each part of this eukaryotic cell."